ts 绕开属性检查的 3 种方法
引言
不知道大家有没有遇到这种情况,当我们预先定义了 ts 的一些类型后,在我们真正用到时却又和原先约定的类型定义不一样,哎?那有时候我们有不想或者因为因为一些情况不好去改原来已经定义过的类型定义,这又该怎么办呢? 不要着急,ts 为我们提供了 3 中解决方案,
请看下面:
示例代码:
interface SquareConfig {
color?: string;
width?: number;
}
function createSquare(config: SquareConfig): { color: string, area: number } {
return {
color: config.color,
area: config.width
}
}
let mySquare = createSquare({ color: 'red', width: 100 })
console.log('mySquare--->', mySquare)
如上所示,声明一个 createSquare 函数,形参类型是 SquareConfig 接口,传入的形参是{ color: "red", width: 100 },好,这个时候是符合我们原先的 ts 类型定义的,但是当我们把入参改为{ color: "red", width12: 100 },这个时候 ts 就会判断出入参传入有误,嘿,还智能的提示一下写 width12 是不是想传 width 这个变量
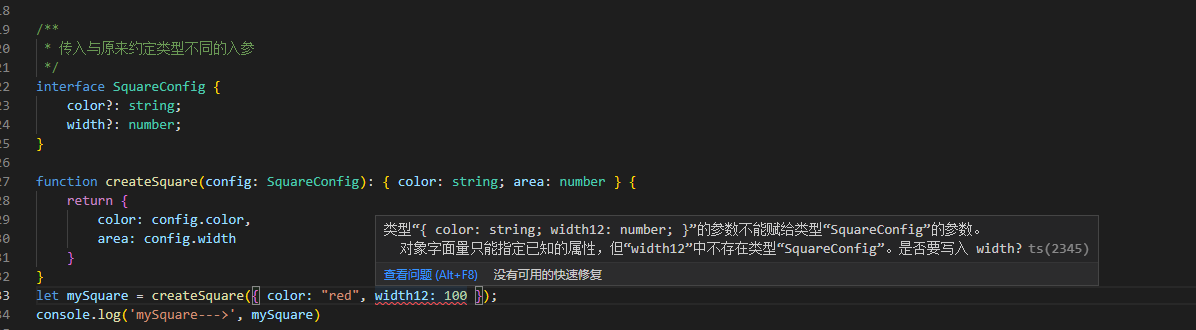
可是,如果我们真的是需要第二参数不同,那该如何嘞,请看下面的 3 种解决方式:
1 类型断言
最简便的方法,用 as 告诉 ts 这就是我想要的,这个类型是对的,好的,那么 ts 就不会报错
interface SquareConfig {
color?: string;
width?: number;
}
function createSquare(config: SquareConfig): { color: string; area: number } {
return {
color: config.color,
area: config.width,
}
}
let mySquare = createSquare({ color: "red", opacity: 0.5 } as SquareConfig); // 这里声明了{ color: "red", opacity: 0.5 } 就是SquareConfig类型
console.log('mySquare--->', mySquare)
2 添加一个字符串索引签名
最佳方式
interface SquareConfig {
color?: string;
width?: number;
[propName: string]: any;
}
function createSquare(config: SquareConfig): { color: string; area: number } {
return {
color: config.color,
area: config.width,
}
}
let mySquare = createSquare({ color: "red", opacity: 0.5 }); //这里依然不会报错
console.log('mySquare--->', mySquare)
3 对象赋值转接一手
interface SquareConfig {
color?: string;
width?: number;
}
function createSquare(config: SquareConfig): { color: string; area: number } {
return {
color: config.color,
area: config.width,
}
}
let squareOptions = { color: "red", opacity: 0.5 } // 用squareOptions变量来转接一下
let mySquare = createSquare(squareOptions); //这里依然不会报错
console.log('mySquare--->', mySquare)
参考:
